iOS在子线程中操作UI会导致刷新延迟卡顿,还会存在潜在的崩溃。而有时候单纯通过查看代码的方式,又很难去判断到底是哪个地方导致了子线程操作UI,因此引出的问题难以排查。
楼主最近维护的一个项目就存在滥用子线程的问题,很多没有必要的地方都新开了线程去做处理操作,导致操作完的回调UI处理也可能是在子线程中,导致了各种隐蔽的坑问题。
在网上查找了一些方法,程序运行的检测是否在子线程中操作了UI,大体的思路为,通过Objective-C的runtime机制,动态将自定义的方法替换掉系统原方法,在自定义方法中去判断当前是否为主线程,若不是则打印log,或直接让程序崩溃,以此定位出具体是哪行代码出现的问题。
关于方法的替换
先看一个最简单的例子,例如,我们想替换掉UIVIewController的viewWillAppear方法,先创建一个UIVIewController类别。
代码实现文件如下:
#import "UIViewController+swizzled.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation UIViewController (swizzled)
+ (void)load
{
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
Class class = [self class];
SEL originalSelector = @selector(viewWillAppear:);
SEL swizzledSelector = @selector(swizzled_viewWillAppear);
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, swizzledSelector);
BOOL didAddMethod =
class_addMethod(class,
originalSelector,
method_getImplementation(swizzledMethod),
method_getTypeEncoding(swizzledMethod));
if (didAddMethod)
{
class_replaceMethod(class,
swizzledSelector,
method_getImplementation(originalMethod),
method_getTypeEncoding(originalMethod));
}
else
{
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
});
}
- (void)swizzled_viewWillAppear
{
NSLog(@"swizzled the method!");
[self swizzled_viewWillAppear];
}
@end
直接将程序跑起来,能看到打印输出:
2016-07-23 10:17:04.972 MTGuard[1122:37741] swizzled the method!
关于这个例子的具体相关内容,可以直接搜索 “method swizzling”,网上有很多好文章详细讲解了这些知识点,在此就不再展开讲了。
开始进入正题。
有些人看了上面的例子可能会问,这样替换方法,那是不是要将每一个方法都这样处理啊?那要实现的代码量岂不是很大?回答当然是否定,具体详细的实现步骤且容楼主一步一步道来。
先新创建一个类,直接继承自NSObject就行了,命名为MainThreadGuard。
实现文件 MainThreadGuard.m,先引入头文件
#import <objc/runtime.h>
#import <objc/message.h>
这个头文件里包含了OC runtime的相关函数。
接下来,在类方法load里做方法替换的处理
+ (void)load
{
// replace method
}
有的人可能会在 + (void)initialize 函数中做处理,具体这两个函数的区别可查看苹果官方文档,反正根据楼主的尝试,load方法是在程序运行之初就会调用到,而initialize方法要在对应的类进行实例化时才会调用到,所以采用前者。
因为我们绝大多数的UI操作对象都为UIView或其子类,所以方法的替换针对UIView进行。
load 方法的实现,先贴完整代码再讲解。
+ (void)load
{
// replace method
id objc_class = objc_getClass("UIView");
Class class = [objc_class class];
NSMutableArray *ignoreMethods = [NSMutableArray arrayWithArray:@[@"retain", @"release", @"dealloc", @".cxx_destruct"]];
unsigned int propertyCount = 0;
objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList(class, &propertyCount);
for(int i = 0; i < propertyCount; i++)
{
objc_property_t property = properties[i];
[ignoreMethods addObject:@(property_getName(property))];
}
free(properties);
unsigned int methodCount = 0;
Method *methodList = class_copyMethodList(class, &methodCount);
for (int i = 0; i < methodCount; i++)
{
Method method = methodList[i];
NSString *methodName = NSStringFromSelector(method_getName(method));
if (![methodName hasPrefix:@"_"])
{
BOOL needIgnore = NO;
for (NSString *ignoreMethod in ignoreMethods)
{
if ([methodName isEqualToString:ignoreMethod])
{
needIgnore = YES;
continue;
}
}
if (!needIgnore)
{
replace(class, methodName);
}
}
}
free(methodList);
}
先是通过类名获取到UIView的Class
id objc_class = objc_getClass("UIView");
Class class = [objc_class class];
新建一个数组,保存不需要替换的方法的方法名称
NSMutableArray *ignoreMethods = [NSMutableArray arrayWithArray:@[@"retain", @"release", @"dealloc", @".cxx_destruct"]];
类属性的获取方法和类的私有方法不进行替换。上面数组里的4个方法若替换会出问题,具体原因没有深究,有兴趣的同学可以探索一下。
将类属性的获取方法忽略
unsigned int propertyCount = 0;
objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList(class, &propertyCount);
for(int i = 0; i < propertyCount; i++)
{
objc_property_t property = properties[i];
[ignoreMethods addObject:@(property_getName(property))];
}
class_copyPropertyList获取到的是类所包含所有属性的数组,数组的个数赋值到propertyCount上,property_getName方法将获取到的属性转换成NSString*,添加到数组里。
感兴趣的可以在for循环里加个打印
printf("property name %d : %s\n", i, name);
可以看到属性列表的打印输出:
property name 0 : _mayRemainFocused
property name 1 : _sensitivitySize
property name 2 : skipsSubviewEnumeration
property name 3 : viewTraversalMark
property name 4 : viewDelegate
property name 5 : monitorsSubtree
property name 6 : backgroundColorSystemColorName
property name 7 : currentScreenScale
property name 8 : maskView
property name 9 : _userInterfaceIdiom
property name 10 : hash
property name 11 : superclass
property name 12 : description
...
获取类的实例方法
unsigned int methodCount = 0;
Method *methodList = class_copyMethodList(class, &methodCount);
若想获取类方法,可以用这种方式:
Method *methodList = class_copyMethodList(object_getClass(class), &methodCount);
遍历每一个方法Method,通过method_getName获取到方法的名称,通过是否有下划线来判断类私有方法,若方法名不需要忽略,则进行替换处理。
for (int i = 0; i < methodCount; i++)
{
Method method = methodList[i];
NSString *methodName = NSStringFromSelector(method_getName(method));
if (![methodName hasPrefix:@"_"])
{
BOOL needIgnore = NO;
for (NSString *ignoreMethod in ignoreMethods) {
if ([methodName isEqualToString:ignoreMethod]) {
needIgnore = YES;
continue;
}
}
if (!needIgnore)
{
replace(class, methodName);
}
}
}
注意:通过class_copyPropertyList和class_copyMethodList获取到的对象需要free掉。
替换过处理的函数实现如下:
static void replace(Class cls, NSString *selectorName)
{
SEL selector = NSSelectorFromString(selectorName);
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, selector);
const char *typeDescription = (char *)method_getTypeEncoding(method);
IMP originalImp = class_getMethodImplementation(cls, selector);
IMP msgForwardIMP = _objc_msgForward;
if (typeDescription[0] == '{')
{
NSMethodSignature *methodSignature = [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:typeDescription];
if ([methodSignature.debugDescription rangeOfString:@"is special struct return? YES"].location != NSNotFound) {
msgForwardIMP = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_stret;
}
}
class_replaceMethod(cls, selector, msgForwardIMP, typeDescription);
if (class_getMethodImplementation(cls, @selector(forwardInvocation:)) != (IMP)myForwardInvocation)
{
class_replaceMethod(cls, @selector(forwardInvocation:), (IMP)myForwardInvocation, typeDescription);
}
if (class_respondsToSelector(cls, selector))
{
NSString *originalSelectorName = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"ORIG_%@", selectorName];
SEL originalSelector = NSSelectorFromString(originalSelectorName);
if(!class_respondsToSelector(cls, originalSelector))
{
class_addMethod(cls, originalSelector, originalImp, typeDescription);
}
}
}
传入参数为Class和要替换的方法名称
通过Class和方法名称获取到对应的Method
SEL selector = NSSelectorFromString(selectorName);
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, selector);
method_getTypeEncoding返回的是一个字符串,用来描述方法的参数、返回值,字符所代表的类型具体可参考官方文档
const char *typeDescription = (char *)method_getTypeEncoding(method);
class_getMethodImplementation获取方法对应的IMP,这里用来保存方法原始的IMP
IMP originalImp = class_getMethodImplementation(cls, selector);
_objc_msgForward用于消息转发,关于消息转发可以参考这篇文章,最浅显的理解方式就是,当将原来的IMP替换成_objc_msgForward时,直接进行消息的转发,调用forwardInvocation:。
IMP msgForwardIMP = _objc_msgForward;
class_replaceMethod 将原来的IMP替换掉
class_replaceMethod(cls, selector, msgForwardIMP, typeDescription);
将forwardInvocation:替换成我们自定义的方法myForwardInvocation,这样在消息重定位时便会运行到myForwardInvocation,在这个方法里做线程的判断处理。
if (class_getMethodImplementation(cls, @selector(forwardInvocation:)) != (IMP)myForwardInvocation)
{
class_replaceMethod(cls, @selector(forwardInvocation:), (IMP)myForwardInvocation, typeDescription);
}
myForwardInvocation的定义为:
static void myForwardInvocation(id slf, SEL selector, NSInvocation *invocation);
参数的定义必须保证和IMP一致,第三个参数定义为NSInvocation* 是要保证和 forwardInvocation: 的参数一致
id (*IMP)(id, SEL, ...)
Ps. IMP使用当前CPU架构实现的标准的C调用约定。第一个参数是指向self的指针(如果是实例方法,则是类实例的内存地址;如果是类方法,则是指向元类的指针),第二个参数是方法选择器(selector),接下来是方法的实际参数列表。
最终将原始IMP重新添加到类中,IMP的方法名称为原始方法名前加前缀ORIG_,后续会通过这个方法名称获取原始的IMP,并将函数进行正常的流程处理
if (class_respondsToSelector(cls, selector))
{
NSString *originalSelectorName = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"ORIG_%@", selectorName];
SEL originalSelector = NSSelectorFromString(originalSelectorName);
if(!class_respondsToSelector(cls, originalSelector))
{
class_addMethod(cls, originalSelector, originalImp, typeDescription);
}
}
myForwardInvocation方法实现如下
static void myForwardInvocation(id slf, SEL selector, NSInvocation *invocation)
{
if (![NSThread currentThread].isMainThread)
{
NSLog(@"%@",[NSThread callStackSymbols]);
}
NSString *selectorName = NSStringFromSelector(invocation.selector);
NSString *origSelectorName = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"ORIG_%@", selectorName];
SEL origSelector = NSSelectorFromString(origSelectorName);
invocation.selector = origSelector;
[invocation invoke];
}
通过[NSThread currentThread].isMainThread判断当前是否为主线程,若不是则打印当前调用栈。
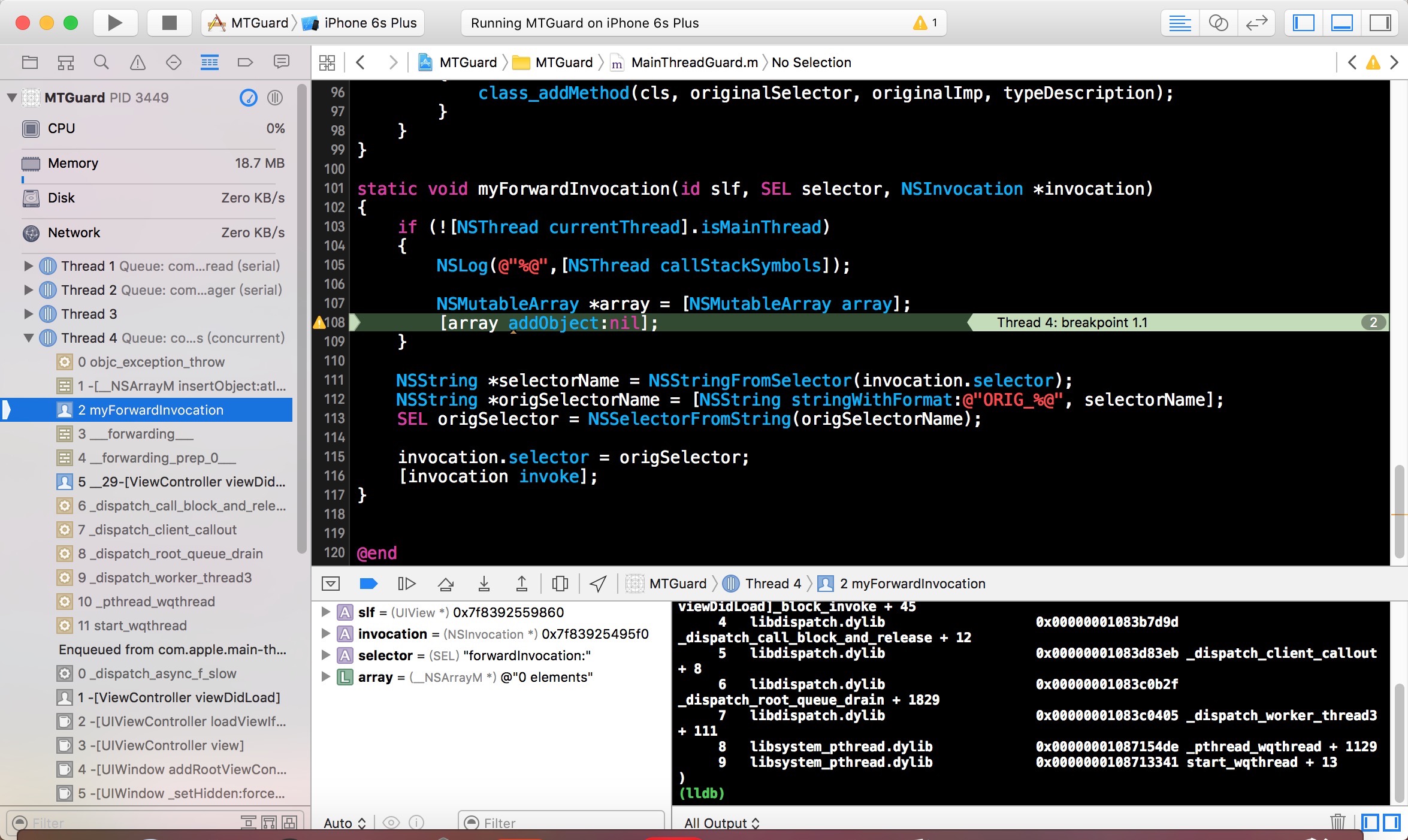
也可以通过数组插入nil的方式,让程序崩溃,打开异常断点进行调试时,若有子线程操作UI情况则会立即崩溃,具体出现问题的代码便一目了然了。
正常执行的时候回通过ORIG_前缀名获取到当前函数的原始方法,此时用原始方法继续运行既和正常的调用一致。
接下来测试一下,随便找个视图控制器加上代码:
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0), ^(){
UIView *v = [UIView new];
[self.view addSubview:v];
});
因为MainThreadGuard在程序运行时便会进行处理,所以并不需要在哪个地方引入头文件。
运行起来,崩溃的地方就能直接看到是在哪个子线程操作UI了:)
最后
使用的时候直接将MainThreadGuard类拖到项目中即可,为了方便专门定义了一个相关的宏,在debug的时候打开即可。
完。